Global Procurement Areas of Reportable Productivity
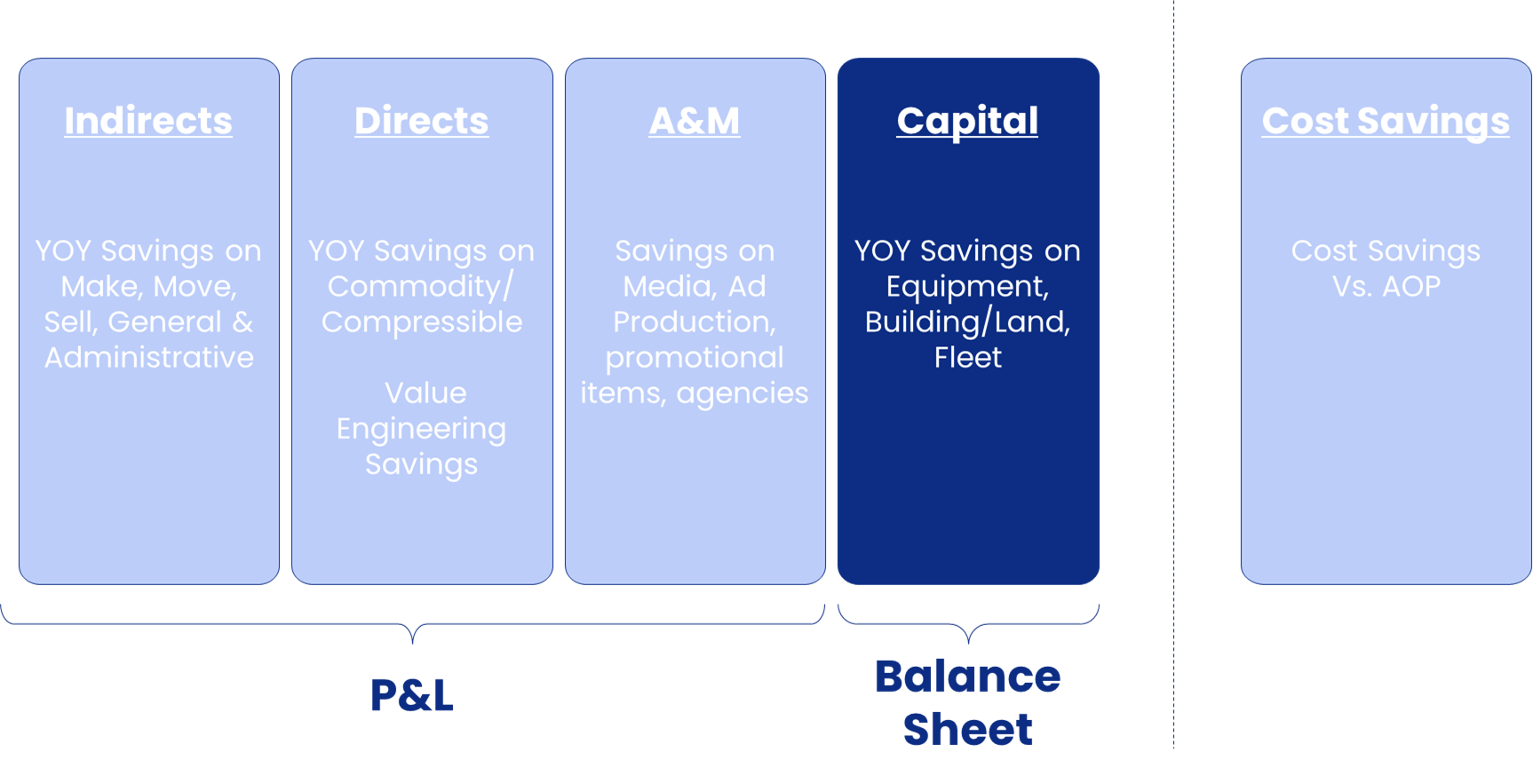
Capital Productivity

Productivity = (YOY change in cost per unit) X (number of units purchased in the Current Year)
Savings may be driven over different timeframes due to the timing of purchases:
- One time (Single Year, buy a PC line)
- Multi-Year (low-cost cooler substitution over 3 years)
- Spend by category is not always repeatable in the same BU (large machines)
- Similar purchases often exceed 2 years
- Productivity baseline may be measured within 2yrs, exception for Capital only
Capital Productivity Guidelines
- Capital Productivity refers to cost reduction initiatives which lead to YoY savings in fixed & variable costs, excluding the impact of leverage; there must be a historical baseline in order for an initiative to qualify as a Productivity initiative.
- YoY Change in Cost per Unit is defined as the Year-over-Year change in the cost of a: Like-for-Like items or YoY Change in Weighted Average Price (WAP) of a group of items having the same fir/form/function.
- Comparable assets purchased in the last two fiscal years in the same Business/Market Unit, if not available then same sector.
- Year over Year change in spend cannot be used as the productivity calculation, the savings must be a result of a year over year cost per unit reduction.
- For substitution multi-year projects, YoY productivity recognized by comparing PY vs CY WAP across the initiative life.
- YoY Productivity incluse of all costs (i.e. inflation, duties, freight and taxes) and rebates.
- Savings are reported based on BU CAPES plan as reported to Global FP&A.
- Includes TCO and must be validated by Business Finance.
Capital Productivity



•Productivity may only be reported if the savings are against in-scope managed spend. If spend is in-scope and is under contract for several years, it is still managed spend.
•Productivity: If Productivity is claimed for some spend (e.g. the Savings is in the numerator of the equation), then the spend must be included in the denominator in the YoY Productivity KPI % formula.
•Personnel Vacancy: If someone has left GP and GP has a temporary vacancy, the spend is still in-scope.
•New Role: If the MSO/COE has approval for a new role covering new spend, the spend will be considered “in-scope” once the vacancy has been occupied.
•Specification/Policy: If the business refuses to change a specification or policy, the spend is still “in-scope” & will remain so unless GP chooses to eliminate the resource from the Category and officially deem it “out-of-scope.”
•Taxes: Taxes that are embedded in spend with the supplier (in covered Categories) are considered “in-scope.” GP does not specifically exclude taxes or tariffs that are already included within a supplier’s spend.
•Fuel: Direct bulk fuel purchases are not generally “in-scope” unless a resource is deployed to support it to generate savings. If the latter is true, the spend is “in-scope.”
•Fragmented Category: If GP has deployed a resource to support a fragment Category and has low visibility into that Category, the associated spend is still considered “in-scope.” It is the responsibility of GP personnel to increase visibility.
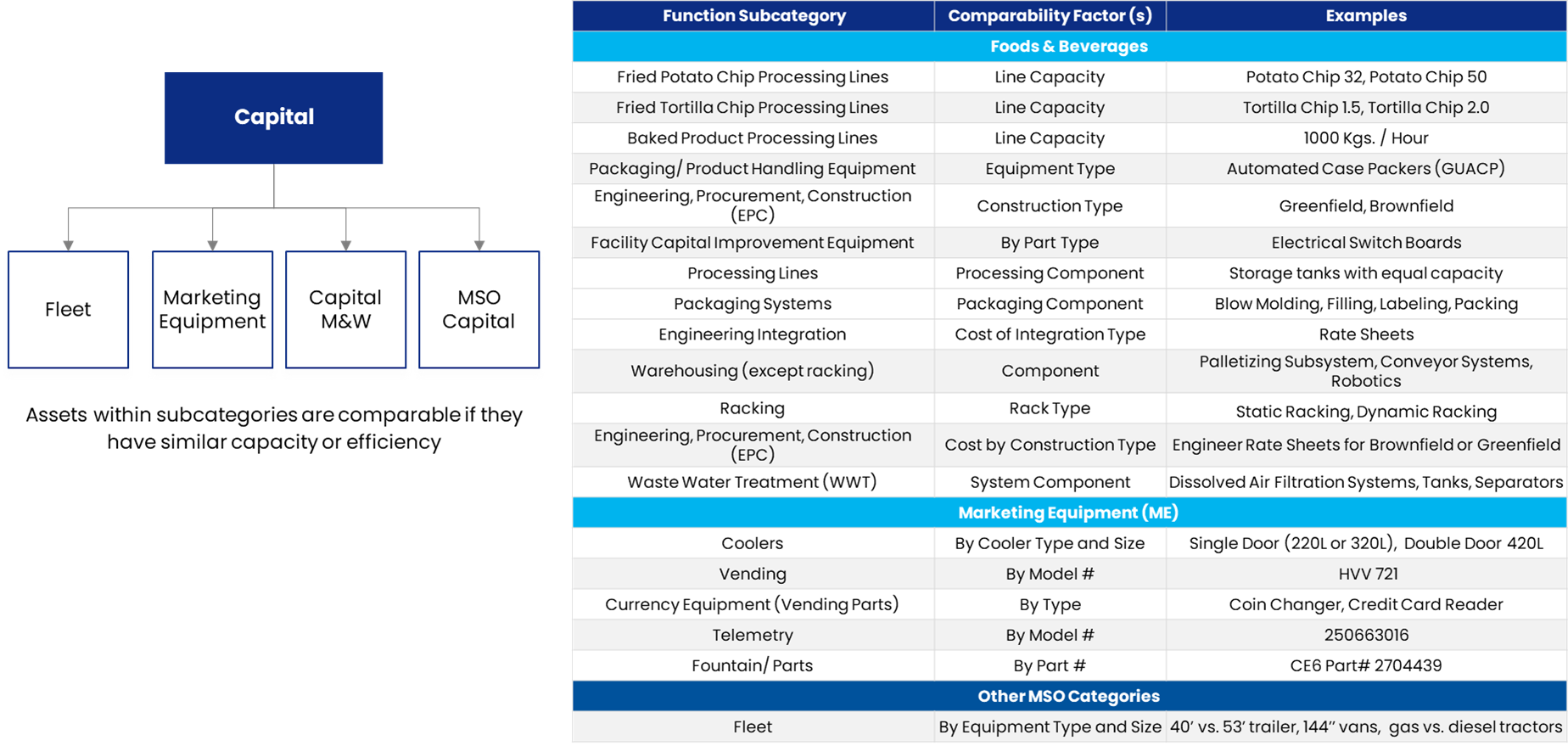
CAPITAL: Fit/Form Criteria for Rate Comparisons